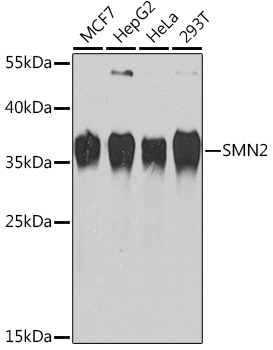
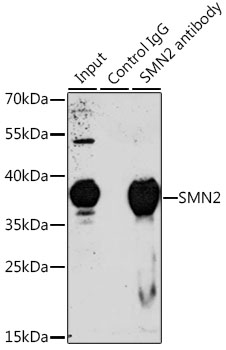
Anti-SMN2 Antibody (CAB1652)
- SKU:
- CAB1652
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Frequently bought together:
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-SMN2 Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CAB1652 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB IHC IF IP |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-197 of human SMN2 (NP_059107.1). |
| 申し込み: | WB IHC IF IP |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 IP 1:50 - 1:100 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| ポジティブサンプル: | MCF7, HepG2, HeLa, 293T |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-197 of human SMN2 (NP_059107.1). |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | MAMS SGGS GGGV PEQE DSVL FRRG TGQS DDSD IWDD TALI KAYD KAVA SFKH ALKN GDIC ETSG KPKT TPKR KPAK KNKS QKKN TAAS LQQW KVGD KCSA IWSE DGCI YPAT IASI DFKR ETCV VVYT GYGN REEQ NLSD LLSP ICEV ANNI EQNA QENE NESQ VSTD ESEN SRSP GNKS DNIK PKSA PWNS FLPP P |
| 遺伝子ID: | 6607 |
| Uniprot: | Q16637 |
| セルラーロケーション: | Cajal body, Cytoplasm, Cytoplasmic granule, Nucleus, Z line, gem, myofibril, sarcomere |
| 計算された分子量: | 27kDa/28kDa/30kDa/31kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 32kDa |
| 同義語: | SMN2, BCD541, C-BCD541, GEMIN1, SMNC, TDRD16B |
| バックグラウンド: | This gene is part of a 500 kb inverted duplication on chromosome 5q13. This duplicated region contains at least four genes and repetitive elements which make it prone to rearrangements and deletions. The repetitiveness and complexity of the sequence have also caused difficulty in determining the organization of this genomic region. The telomeric and centromeric copies of this gene are nearly identical and encode the same protein. While mutations in the telomeric copy are associated with spinal muscular atrophy, mutations in this gene, the centromeric copy, do not lead to disease. This gene may be a modifier of disease caused by mutation in the telomeric copy. The critical sequence difference between the two genes is a single nucleotide in exon 7, which is thought to be an exon splice enhancer. Note that the nine exons of both the telomeric and centromeric copies are designated historically as exon 1, 2a, 2b, and 3-8. It is thought that gene conversion events may involve the two genes, leading to varying copy numbers of each gene. The full length protein encoded by this gene localizes to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Within the nucleus, the protein localizes to subnuclear bodies called gems which are found near coiled bodies containing high concentrations of small ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). This protein forms heteromeric complexes with proteins such as SIP1 and GEMIN4, and also interacts with several proteins known to be involved in the biogenesis of snRNPs, such as hnRNP U protein and the small nucleolar RNA binding protein. Four transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SMN: The SMN complex plays an essential role in spliceosomal snRNP assembly in the cytoplasm and is required for pre-mRNA splicing in the nucleus. It may also play a role in the metabolism of snoRNPs. Defects in SMN1 are the cause of spinal muscular atrophy autosomal recessive type 1 (SMA1). Spinal muscular atrophy refers to a group of neuromuscular disorders characterized by degeneration of the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord, leading to symmetrical muscle weakness and atrophy. Autosomal recessive forms are classified according to the age of onset, the maximum muscular activity achieved, and survivorship. The severity of the disease is mainly determined by the copy number of SMN2, a copy gene which predominantly produces exon 7-skipped transcripts and only low amount of full-length transcripts that encode for a protein identical to SMN1. Only about 4% of SMA patients bear one SMN1 copy with an intragenic mutation. SMA1 is a severe form, with onset before 6 months of age. SMA1 patients never achieve the ability to sit. Defects in SMN1 are the cause of spinal muscular atrophy autosomal recessive type 2 (SMA2). SMA2 is an autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy of intermediate severity, with onset between 6 and 18 months. Patients do not reach the motor milestone of standing, and survive into adulthood. Defects in SMN1 are the cause of spinal muscular atrophy autosomal recessive type 3 (SMA3). SMA3 is an autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy with onset after 18 months. SMA3 patients develop ability to stand and walk and survive into adulthood. Defects in SMN1 are the cause of spinal muscular atrophy autosomal recessive type 4 (SMA4). SMA4 is an autosomal recessive spinal muscular atrophy characterized by symmetric proximal muscle weakness with onset in adulthood and slow disease progression. SMA4 patients can stand and walk. Belongs to the SMN family. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:RNA processing; RNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 5q13.2 Cellular Component: Cajal body; cytoplasm; cytosol; neuron projection; nucleoplasm; nucleus; perikaryon; SMN complex Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein binding Biological Process: nuclear import; spliceosomal snRNP biogenesis; spliceosome assembly; transcription termination Disease: Spinal Muscular Atrophy, Type I; Spinal Muscular Atrophy, Type Ii; Spinal Muscular Atrophy, Type Iii; Spinal Muscular Atrophy, Type Iv |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is part of a 500 kb inverted duplication on chromosome 5q13. This duplicated region contains at least four genes and repetitive elements which make it prone to rearrangements and deletions. The repetitiveness and complexity of the sequence have also caused difficulty in determining the organization of this genomic region. The telomeric and centromeric copies of this gene are nearly identical and encode the same protein. While mutations in the telomeric copy are associated with spinal muscular atrophy, mutations in this gene, the centromeric copy, do not lead to disease. This gene may be a modifier of disease caused by mutation in the telomeric copy. The critical sequence difference between the two genes is a single nucleotide in exon 7, which is thought to be an exon splice enhancer. Note that the nine exons of both the telomeric and centromeric copies are designated historically as exon 1, 2a, 2b, and 3-8. It is thought that gene conversion events may involve the two genes, leading to varying copy numbers of each gene. The full length protein encoded by this gene localizes to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Within the nucleus, the protein localizes to subnuclear bodies called gems which are found near coiled bodies containing high concentrations of small ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). This protein forms heteromeric complexes with proteins such as SIP1 and GEMIN4, and also interacts with several proteins known to be involved in the biogenesis of snRNPs, such as hnRNP U protein and the small nucleolar RNA binding protein. Four transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q16637 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2498924 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6607 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q16637.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q16637,Q13119, Q549U5, Q96J51, A8K0V4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q16637 |
| Molecular Weight: | 32kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Survival motor neuron protein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | survival of motor neuron 2, centromeric |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SMN2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SMNC; BCD541; GEMIN1; TDRD16B; C-BCD541 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | survival motor neuron protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Survival motor neuron protein |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Component of gems 1; Gemin-1 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SMN1 |
View AllClose