Anti-Phospho-PRKCA (T638) Antibody (RACO0111)
- SKU:
- RACO0111
- Product type:
- Recombinant Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Human
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Application:
- WB
- Application:
- IF
- Application:
- ELISA
- Conjugation:
- Unconjugated
Description
| 商品名: | Phospho-PRKCA (T638) Antibody |
| Product SKU: | RACO0111 |
| サイズ: | 50ul |
| 宿主種: | Human |
| 申し込み: | ELISA, WB, IF |
| 推奨される希釈: | WB:1:500-1:5000, IF:1:20-1:200 |
| 反応性: | Human |
| 免疫原: | A synthesized peptide derived from human Phospho-PRKCA (T638) |
| 憲法: | Liquid |
| ストレージバッファ: | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
| 精製方法: | Affinity-chromatography |
| 抗体のクローン性: | Monoclonal |
| アイソタイプ: | Rabbit IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| バックグラウンド: | Calcium-activated, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that is involved in positive and negative regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, migration and adhesion, tumorigenesis, cardiac hypertrophy, angiogenesis, platelet function and inflammation, by directly phosphorylating targets such as RAF1, BCL2, CSPG4, TNNT2/CTNT, or activating signaling cascade involving MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2) and RAP1GAP. Involved in cell proliferation and cell growth arrest by positive and negative regulation of the cell cycle. Can promote cell growth by phosphorylating and activating RAF1, which mediates the activation of the MAPK/ERK signaling cascade, and/or by up-regulating CDKN1A, which facilitates active cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) complex formation in glioma cells. In intestinal cells stimulated by the phorbol ester PMA, can trigger a cell cycle arrest program which is associated with the accumulation of the hyper-phosphorylated growth-suppressive form of RB1 and induction of the CDK inhibitors CDKN1A and CDKN1B. Exhibits anti-apoptotic function in glioma cells and protects them from apoptosis by suppressing the p53/TP53-mediated activation of IGFBP3, and in leukemia cells mediates anti-apoptotic action by phosphorylating BCL2. During macrophage differentiation induced by macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF1), is translocated to the nucleus and is associated with macrophage development. After wounding, translocates from focal contacts to lamellipodia and participates in the modulation of desmosomal adhesion. Plays a role in cell motility by phosphorylating CSPG4, which induces association of CSPG4 with extensive lamellipodia at the cell periphery and polarization of the cell accompanied by increases in cell motility. During chemokine-induced CD4(+) T cell migration, phosphorylates CDC42-guanine exchange factor DOCK8 resulting in its dissociation from LRCH1 and the activation of GTPase CDC42 (PubMed:28028151). Is highly expressed in a number of cancer cells where it can act as a tumor promoter and is implicated in malignant phenotypes of several tumors such as gliomas and breast cancers. Negatively regulates myocardial contractility and positively regulates angiogenesis, platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in arteries. Mediates hypertrophic growth of neonatal cardiomyocytes, in part through a MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2)-dependent signaling pathway, and upon PMA treatment, is required to induce cardiomyocyte hypertrophy up to heart failure and death, by increasing protein synthesis, protein-DNA ratio and cell surface area. Regulates cardiomyocyte function by phosphorylating cardiac troponin T (TNNT2/CTNT), which induces significant reduction in actomyosin ATPase activity, myofilament calcium sensitivity and myocardial contractility. In angiogenesis, is required for full endothelial cell migration, adhesion to vitronectin (VTN), and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA)-dependent regulation of kinase activation and vascular tube formation. Involved in the stabilization of VEGFA mRNA at post-transcriptional level and mediates VEGFA-induced cell proliferation. In the regulation of calcium-induced platelet aggregation, mediates signals from the CD36/GP4 receptor for granule release, and activates the integrin heterodimer ITGA2B-ITGB3 through the RAP1GAP pathway for adhesion. During response to lipopolysaccharides (LPS), may regulate selective LPS-induced macrophage functions involved in host defense and inflammation. But in some inflammatory responses, may negatively regulate NF-kappa-B-induced genes, through IL1A-dependent induction of NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (NFKBIA/IKBA). Upon stimulation with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), phosphorylates EIF4G1, which modulates EIF4G1 binding to MKNK1 and may be involved in the regulation of EIF4E phosphorylation. Phosphorylates KIT, leading to inhibition of KIT activity. Phosphorylates ATF2 which promotes cooperation between ATF2 and JUN, activating transcription. |
| シノニム: | Protein kinase C alpha type, PKC-A, PKC-alpha, PRKCA, PKCA, PRKACA |
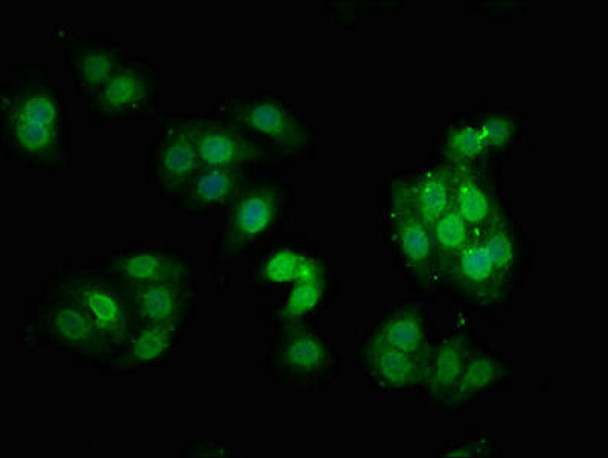
 | Immunofluorescence staining of HepG2 cells with RACO0111 at 1:100,counter-stained with DAPI. The cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde, permeabilized using 0.2% Triton X-100 and blocked in 10% normal Goat Serum. The cells were then incubated with the antibody overnight at 4°C. The secondary antibody was Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L). |
 | Western Blot. Positive WB detected in Hela whole cell lysate A549 whole cell lysate treated with Calyculin A or EGF). All lanes Phospho-PRKCA antibody at 0.68µg/ml. Secondary. Goat polyclonal to rabbit IgG at 1:50000 dilution. Predicted band size: 80 KDa. Observed band size: 80 KDa. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PKCA: an AGC kinase of the PKC family. A classical PKC downstream of many mitogenic and receptors. Classical PKCs are calcium-dependent enzymes that are activated by phosphatidylserine, diacylglycerol and phorbol esters. Contains a pseudo-substrate autoinhibitory domain that binds to the catalytic domain preventing its activation in the absence of cofactors or activators. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 2.7.11.13; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); Oncoprotein; Kinase, protein; Protein kinase, AGC; AGC group; PKC family; Alpha subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q22-q23.2 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; photoreceptor outer segment; mitochondrion; cell soma; endoplasmic reticulum; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; apical part of cell; mitochondrial membrane; dendrite; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; cytosol Molecular Function:protein serine/threonine kinase activity; protein binding; enzyme binding; protein kinase C activity; zinc ion binding; calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity; ATP binding; protein kinase activity Biological Process: phototransduction, visible light; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; positive regulation of cell adhesion; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; regulation of muscle contraction; mitotic nuclear envelope disassembly; positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway; signal transduction; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle; protein amino acid phosphorylation; induction of positive chemotaxis; synaptic transmission; negative regulation of cell proliferation; chondrocyte differentiation; angiogenesis; cell adhesion; positive regulation of macrophage differentiation; regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; regulation of the force of heart contraction; inactivation of MAPK activity; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; platelet activation; neutrophil chemotaxis; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; adenylate cyclase activation; negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity; cellular calcium ion homeostasis; rhodopsin mediated signaling; negative regulation of glucose import; positive regulation of angiogenesis; regulation of rhodopsin mediated signaling; phospholipase C activation; energy reserve metabolic process; innate immune response; gene expression; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; mitotic cell cycle; blood coagulation; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; regulation of insulin secretion; positive regulation of cell migration; positive regulation of inflammatory response |
| NCBI Summary: | Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of serine- and threonine-specific protein kinases that can be activated by calcium and the second messenger diacylglycerol. PKC family members phosphorylate a wide variety of protein targets and are known to be involved in diverse cellular signaling pathways. PKC family members also serve as major receptors for phorbol esters, a class of tumor promoters. Each member of the PKC family has a specific expression profile and is believed to play a distinct role in cells. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the PKC family members. This kinase has been reported to play roles in many different cellular processes, such as cell adhesion, cell transformation, cell cycle checkpoint, and cell volume control. Knockout studies in mice suggest that this kinase may be a fundamental regulator of cardiac contractility and Ca(2+) handling in myocytes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P17252 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 317373571 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5578 |
| NCBI Accession: | P17252.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P17252,Q15137, Q32M72, Q96RE4, B5BU22, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P17252 |
| Molecular Weight: | 76,750 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Protein kinase C alpha type |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | protein kinase C, alpha |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PRKCA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | AAG6; PKCA; PRKACA; PKC-alpha |
| NCBI Protein Information: | protein kinase C alpha type; PKC-A; aging-associated gene 6 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Protein kinase C alpha type |
| Protein Family: | Protein kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PRKCA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | KPCA_HUMAN |