Anti-Ubiquitin Antibody (CAB0162)
- SKU:
- CAB0162
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-Ubiquitin Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CAB0162 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | A synthetic peptide of human Ubiquitin |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:1000 - 1:2000 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
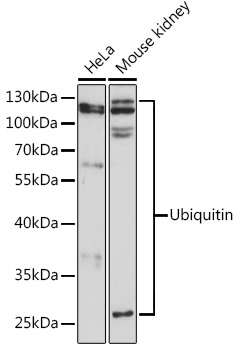
| ポジティブサンプル: | HeLa, Mouse kidney |
| 免疫原: | A synthetic peptide of human Ubiquitin |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | Email for sequence |
| 遺伝子ID: | 7314 |
| Uniprot: | P0CG47 |
| セルラーロケーション: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| 計算された分子量: | 25kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 26KDa/37KDa/60KDa/80KDa/115KDa |
| 同義語: | HEL-S-50, Ubiquitin, UBB |
| バックグラウンド: | This gene encodes ubiquitin, one of the most conserved proteins known. Ubiquitin has a major role in targeting cellular proteins for degradation by the 26S proteosome. It is also involved in the maintenance of chromatin structure, the regulation of gene expression, and the stress response. Ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor protein consisting of either polyubiquitin chains or a single ubiquitin moiety fused to an unrelated protein. This gene consists of three direct repeats of the ubiquitin coding sequence with no spacer sequence. Consequently, the protein is expressed as a polyubiquitin precursor with a final amino acid after the last repeat. An aberrant form of this protein has been detected in patients with Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on chromosomes 1, 2, 13, and 17. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | UBB: Ubiquitin exists either covalently attached to another protein, or free (unanchored). When covalently bound, it is conjugated to target proteins via an isopeptide bond either as a monomer (monoubiquitin), a polymer linked via different Lys residues of the ubiquitin (polyubiquitin chains) or a linear polymer linked via the initiator Met of the ubiquitin (linear polyubiquitin chains). Polyubiquitin chains, when attached to a target protein, have different functions depending on the Lys residue of the ubiquitin that is linked: Lys-6-linked may be involved in DNA repair; Lys-11-linked is involved in ERAD (endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation) and in cell-cycle regulation; Lys-29-linked is involved in lysosomal degradation; Lys-33-linked is involved in kinase modification; Lys-48-linked is involved in protein degradation via the proteasome; Lys-63-linked is involved in endocytosis, DNA-damage responses as well as in signaling processes leading to activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa-B. Linear polymer chains formed via attachment by the initiator Met lead to cell signaling. Ubiquitin is usually conjugated to Lys residues of target proteins, however, in rare cases, conjugation to Cys or Ser residues has been observed. When polyubiquitin is free (unanchored-polyubiquitin), it also has distinct roles, such as in activation of protein kinases, and in signaling. Belongs to the ubiquitin family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Apoptosis; Ubiquitin-like modifier; Cell development/differentiation; Cell cycle regulation; Transcription regulation; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17p12-p11.2 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; neuron projection; cell soma; mitochondrion; plasma membrane; endosome membrane; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding Biological Process: circadian rhythm; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; protein polyubiquitination; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; viral reproduction; positive regulation of apoptosis; activation of MAPK activity; stress-activated MAPK cascade; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; endosome transport; T cell receptor signaling pathway; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; mitochondrion transport along microtubule; regulation of apoptosis; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; JNK cascade; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; regulation of interferon type I production; glycogen biosynthetic process; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; transcription, DNA-dependent; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I, TAP-dependent; glucose metabolic process; Notch receptor processing; virus assembly; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; carbohydrate metabolic process; viral protein processing; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; negative regulation of interferon type I production; negative regulation of apoptosis; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; apoptosis; pathogenesis; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; viral infectious cycle; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; anaphase-promoting complex-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; positive regulation of interferon type I production; transmembrane transport; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; Notch signaling pathway; cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; DNA repair; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; innate immune response; gene expression; mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; neurite morphogenesis Disease: Cleft Palate, Isolated |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes ubiquitin, one of the most conserved proteins known. Ubiquitin has a major role in targeting cellular proteins for degradation by the 26S proteosome. It is also involved in the maintenance of chromatin structure, the regulation of gene expression, and the stress response. Ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor protein consisting of either polyubiquitin chains or a single ubiquitin moiety fused to an unrelated protein. This gene consists of three direct repeats of the ubiquitin coding sequence with no spacer sequence. Consequently, the protein is expressed as a polyubiquitin precursor with a final amino acid after the last repeat. An aberrant form of this protein has been detected in patients with Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on chromosomes 1, 2, 13, and 17. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013] |
| UniProt Code: | P0CG47 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 302595875 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7314 |
| NCBI Accession: | P0CG47.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P0CG47,P0CG48, P62979, P62987, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P0CG47 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Polyubiquitin-B |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ubiquitin B |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | UBB |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HEL-S-50 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | polyubiquitin-B |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Polyubiquitin-B |
| Protein Family: | Ubiquilin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | UBB |
| UniProt Entry Name: | UBB_HUMAN |