Anti-SPAST Antibody (CAB9543)
- SKU:
- CAB9543
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Application:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Cycle
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-SPAST Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CAB9543 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 120-325 of human SPAST (NP_055761.2). |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
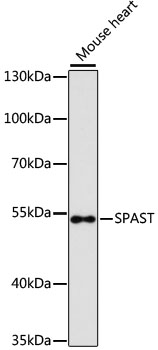
| ポジティブサンプル: | Mouse heart |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 120-325 of human SPAST (NP_055761.2). |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | HKQA FEYI SIAL RIDE DEKA GQKE QAVE WYKK GIEE LEKG IAVI VTGQ GEQC ERAR RLQA KMMT NLVM AKDR LQLL EKMQ PVLP FSKS QTDV YNDS TNLA CRNG HLQS ESGA VPKR KDPL THTS NSLP RSKT VMKT GSAG LSGH HRAP SYSG LSMV SGVK QGSG PAPT THKG TPKT NRTN KPST PTTA TRKK KDLK NFRN VDSN LA |
| 遺伝子ID: | 6683 |
| Uniprot: | Q9UBP0 |
| セルラーロケーション: | Cytoplasm, Endoplasmic reticulum, Endosome, Membrane, Nucleus, Single-pass membrane protein, centrosome, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, perinuclear region, spindle |
| 計算された分子量: | 54kDa/58kDa/63kDa/67kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 52kDa |
| 同義語: | SPAST, ADPSP, FSP2, SPG4, spastin |
| バックグラウンド: | This gene encodes a member of the AAA (ATPases associated with a variety of cellular activities) protein family. Members of this protein family share an ATPase domain and have roles in diverse cellular processes including membrane trafficking, intracellular motility, organelle biogenesis, protein folding, and proteolysis. The encoded ATPase may be involved in the assembly or function of nuclear protein complexes. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Other alternative splice variants have been described but their full length sequences have not been determined. Mutations associated with this gene cause the most frequent form of autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia 4. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | spastin: ATP-dependent microtubule severing protein. Microtubule severing may promote reorganization of cellular microtubule arrays and the release of microtubules from the centrosome following nucleation. Required for membrane traffic from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi and for completion of the abscission stage of cytokinesis. May also play a role in axon growth and the formation of axonal branches. Defects in SPAST are the cause of spastic paraplegia autosomal dominant type 4 (SPG4). Spastic paraplegia is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. SPG4 is the most common form of autosomal dominant spastic paraplegias. Belongs to the AAA ATPase family. Spastin subfamily. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative promoter. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cytoskeletal; EC 3.6.4.3; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2p24-p21 Cellular Component: microtubule cytoskeleton; microtubule; centrosome; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; endoplasmic reticulum; cytoplasm; integral to membrane; spindle; cytoplasmic vesicle; midbody; nucleus; endosome Molecular Function:protein binding; microtubule binding; beta-tubulin binding; microtubule-severing ATPase activity; alpha-tubulin binding; ATP binding Biological Process: positive regulation of microtubule depolymerization; ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport; axonogenesis; metabolic process; microtubule severing; microtubule bundle formation; protein homooligomerization; cytoplasmic microtubule organization and biogenesis Disease: Spastic Paraplegia 4, Autosomal Dominant |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the AAA (ATPases associated with a variety of cellular activities) protein family. Members of this protein family share an ATPase domain and have roles in diverse cellular processes including membrane trafficking, intracellular motility, organelle biogenesis, protein folding, and proteolysis. The encoded ATPase may be involved in the assembly or function of nuclear protein complexes. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Other alternative splice variants have been described but their full length sequences have not been determined. Mutations associated with this gene cause the most frequent form of autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia 4. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9UBP0 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 40806170 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6683 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_955468.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9UBP0,Q9UPR9, A7E2A7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9UBP0 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1493.57 |
| NCBI Full Name: | spastin isoform 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | spastin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SPAST |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FSP2; SPG4; ADPSP |
| NCBI Protein Information: | spastin; spastic paraplegia 4 protein; spastic paraplegia 4 (autosomal dominant; spastin) |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Spastin |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Spastic paraplegia 4 protein |
| Protein Family: | Spastin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SPAST |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SPAST_HUMAN |