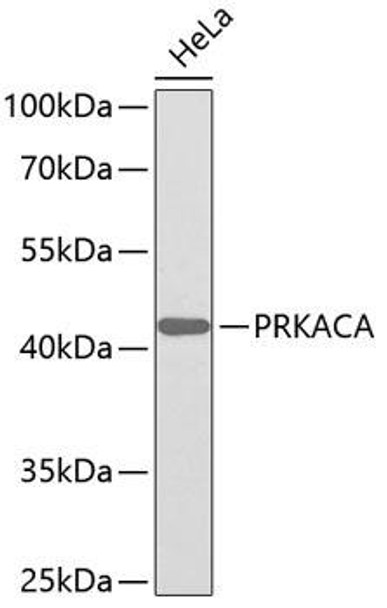
Anti-PRKACA Antibody (CAB0798)
- SKU:
- CAB0798
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-PRKACA Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CAB0798 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 20uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB IHC |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | A synthetic peptide of human PRKACA |
| 申し込み: | WB IHC |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
| ポジティブサンプル: | HeLa |
| 免疫原: | A synthetic peptide of human PRKACA |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | Email for sequence |
| 遺伝子ID: | 5566 |
| Uniprot: | P17612 |
| セルラーロケーション: | Cell membrane, Cell projection, Cytoplasm, Lipid-anchor, Membrane, Mitochondrion, Nucleus, cilium, flagellum |
| 計算された分子量: | 39kDa/40kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 41kDa |
| 同義語: | PRKACA, PKACA, PPNAD4 |
| バックグラウンド: | This gene encodes one of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A, which exists as a tetrameric holoenzyme with two regulatory subunits and two catalytic subunits, in its inactive form. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinase A is important to many cellular processes, including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Constitutive activation of this gene caused either by somatic mutations, or genomic duplications of regions that include this gene, have been associated with hyperplasias and adenomas of the adrenal cortex and are linked to corticotropin-independent Cushing's syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Tissue-specific isoforms that differ at the N-terminus have been described, and these isoforms may differ in the post-translational modifications that occur at the N-terminus of some isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PKACA: catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase alpha, an AGC kinase. A number of inactive tetrameric holoenzymes are produced by the combination of homo- or heterodimers of the different regulatory subunits associated with two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Two splice-variant isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, AGC; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); Kinase, protein; EC 2.7.11.11; AGC group; PKA family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19p13.1 Cellular Component: centrosome; membrane; mitochondrion; plasma membrane; cytosol; nucleus; neuromuscular junction; AMP-activated protein kinase complex; cAMP-dependent protein kinase complex Molecular Function:protein binding; cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity; ubiquitin protein ligase binding; protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity; protein kinase binding; ATP binding Biological Process: nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; water transport; pathogenesis; signal transduction; protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of protein export from nucleus; triacylglycerol catabolic process; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; transmembrane transport; sperm capacitation; regulation of synaptic transmission; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; cytosolic calcium ion homeostasis; regulation of osteoblast differentiation; regulation of heart rate; organelle organization and biogenesis; activation of protein kinase A; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation; glucose metabolic process; gluconeogenesis; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; mesoderm formation; phospholipase C activation; regulation of protein binding; neural tube closure; carbohydrate metabolic process; energy reserve metabolic process; innate immune response; renal water homeostasis; mitotic cell cycle; blood coagulation; regulation of insulin secretion |
| NCBI Summary: | cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive kinase holoenzyme is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family and is a catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P17612 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 125205 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5566 |
| NCBI Accession: | P17612.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P17612,Q32P54, Q9H2Y0, Q9NRB4, Q9NRH9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P17612 |
| Molecular Weight: | 39,953 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, alpha |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PRKACA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PKACA |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha; PKA C-alpha; protein kinase A catalytic subunit; cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha, isoform 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| Protein Family: | cAMP-dependent protein kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PRKACA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | KAPCA_HUMAN |