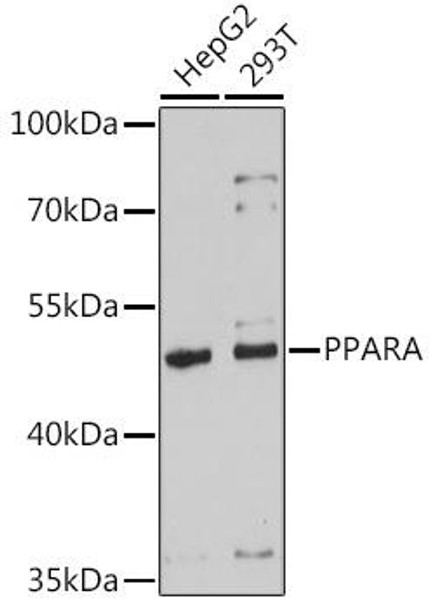
Anti-PPARA Antibody (CAB18252)
- SKU:
- CAB18252
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-PPARA Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CAB18252 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant protein of human PPARA. |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
| ポジティブサンプル: | HepG2, 293T |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant protein of human PPARA. |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | Email for sequence |
| 遺伝子ID: | 5465 |
| Uniprot: | Q07869 |
| セルラーロケーション: | |
| 計算された分子量: | 52kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 52kDa |
| 同義語: | PPAR, NR1C1, hPPAR, PPARalpha, PPAR alpha, PPARA |
| バックグラウンド: | Peroxisome proliferators include hypolipidemic drugs, herbicides, leukotriene antagonists, and plasticizers; this term arises because they induce an increase in the size and number of peroxisomes. Peroxisomes are subcellular organelles found in plants and animals that contain enzymes for respiration and for cholesterol and lipid metabolism. The action of peroxisome proliferators is thought to be mediated via specific receptors, called PPARs, which belong to the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. PPARs affect the expression of target genes involved in cell proliferation, cell differentiation and in immune and inflammation responses. Three closely related subtypes (alpha, beta/delta, and gamma) have been identified. This gene encodes the subtype PPAR-alpha, which is a nuclear transcription factor. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene, although the full-length nature of only two has been determined. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PPAR-alpha: Ligand-activated transcription factor. Key regulator of lipid metabolism. Activated by the endogenous ligand 1-palmitoyl- 2-oleoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphocholine (16:0/18:1-GPC). Activated by oleylethanolamide, a naturally occurring lipid that regulates satiety. Receptor for peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Regulates the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Functions as transcription activator for the ACOX1 and P450 genes. Transactivation activity requires heterodimerization with RXRA and is antagonized by NR2C2. Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Nuclear receptor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q13.31 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein domain specific binding; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor activity; NFAT protein binding; zinc ion binding; drug binding; phosphatase binding; protein binding; DNA binding; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding; sequence-specific DNA binding; protein complex binding; steroid hormone receptor activity; transcription factor activity; lipid binding Biological Process: circadian rhythm; epidermis development; wound healing; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; heart development; behavioral response to nicotine; cellular lipid metabolic process; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; fatty acid metabolic process; negative regulation of appetite; response to insulin stimulus; positive regulation of gluconeogenesis; negative regulation of blood pressure; circadian regulation of gene expression; negative regulation of glycolysis; negative regulation of protein binding; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter; intracellular receptor-mediated signaling pathway; lipoprotein metabolic process; regulation of circadian rhythm; positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation; positive regulation of fatty acid oxidation; response to hypoxia; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; gene expression; steroid hormone mediated signaling; lipid metabolic process; fatty acid transport |
| NCBI Summary: | Peroxisome proliferators include hypolipidemic drugs, herbicides, leukotriene antagonists, and plasticizers; this term arises because they induce an increase in the size and number of peroxisomes. Peroxisomes are subcellular organelles found in plants and animals that contain enzymes for respiration and for cholesterol and lipid metabolism. The action of peroxisome proliferators is thought to be mediated via specific receptors, called PPARs, which belong to the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. PPARs affect the expression of target genes involved in cell proliferation, cell differentiation and in immune and inflammation responses. Three closely related subtypes (alpha, beta/delta, and gamma) have been identified. This gene encodes the subtype PPAR-alpha, which is a nuclear transcription factor. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene, although the full-length nature of only two has been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q07869 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 3041727 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5465 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q07869.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q07869,Q16241, Q6I9S0, Q92486, Q92689, Q9Y3N1, B0G0X3 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q07869 |
| Molecular Weight: | 468 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PPARA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PPAR; NR1C1; hPPAR; PPARalpha |
| NCBI Protein Information: | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; PPAR-alpha; nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 1; peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, alpha; peroxisome proliferator-activated nuclear receptor alpha variant 3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 1 |
| Protein Family: | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PPARA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PPARA_HUMAN |