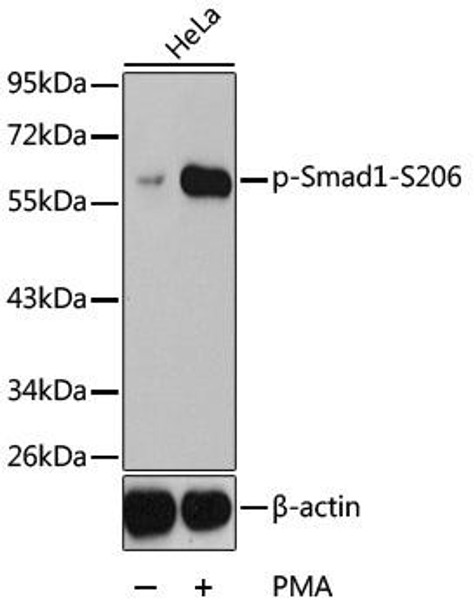
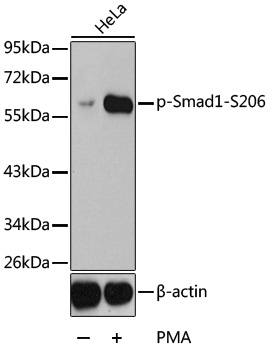
Anti-Phospho-SMAD1-S206 Antibody (CABP0295)
- SKU:
- CABP0295
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Application:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-Phospho-SMAD1-S206 Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CABP0295 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 50uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S206 of human Smad1 |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| ポジティブサンプル: | HeLa |
| 免疫原: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S206 of human Smad1 |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | Email for sequence |
| 遺伝子ID: | 4086 |
| Uniprot: | Q15797 |
| セルラーロケーション: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| 計算された分子量: | 15kDa/52kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 60kDa |
| 同義語: | BSP-1, BSP1, JV4-1, JV41, MADH1, MADR1, Smad1, SMAD1 |
| バックグラウンド: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. This protein mediates the signals of the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are involved in a range of biological activities including cell growth, apoptosis, morphogenesis, development and immune responses. In response to BMP ligands, this protein can be phosphorylated and activated by the BMP receptor kinase. The phosphorylated form of this protein forms a complex with SMAD4, which is important for its function in the transcription regulation. This protein is a target for SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin ligases, such as SMURF1 and SMURF2, and undergoes ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SMAD1: transcription factor phosphorylated and activated by bone morphogenetic protein type 1 receptor kinases. Participates in a wide range of critical processes including morphogenesis, cell-fate determination, proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Phosphorylated forms dimerize with collaborating Smad4 and are translocated into the nucleus, where the transcription of target genes is stimulated. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4q31 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; transcription factor complex; protein complex; cytoplasm; integral to membrane; nuclear inner membrane; intracellular; cytosol; nucleus Molecular Function:identical protein binding; protein binding; metal ion binding; receptor signaling protein activity; protein kinase binding; transcription factor activity; transforming growth factor beta receptor, pathway-specific cytoplasmic mediator activity Biological Process: wound healing; cardiac muscle cell proliferation; primary microRNA processing; embryonic pattern specification; signal transduction; protein amino acid phosphorylation; mesodermal cell fate commitment; BMP signaling pathway; negative regulation of cell proliferation; homeostatic process; ureteric bud development; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; midbrain development; inflammatory response; hindbrain development; response to drug; transcription, DNA-dependent; MAPKKK cascade; positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis; response to organic nitrogen; SMAD protein complex assembly; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation; gamete generation; cartilage development; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; osteoblast fate commitment |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. This protein mediates the signals of the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are involved in a range of biological activities including cell growth, apoptosis, morphogenesis, development and immune responses. In response to BMP ligands, this protein can be phosphorylated and activated by the BMP receptor kinase. The phosphorylated form of this protein forms a complex with SMAD4, which is important for its function in the transcription regulation. This protein is a target for SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin ligases, such as SMURF1 and SMURF2, and undergoes ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q15797 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 13633915 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4086 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q15797.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q15797,Q16636, Q9UFT8, A8KAJ0, D3DNZ9, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q15797 |
| Molecular Weight: | 465 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | SMAD family member 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SMAD1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BSP1; JV41; BSP-1; JV4-1; MADH1; MADR1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1; MAD homolog 1; Mad-related protein 1; TGF-beta signaling protein 1; mothers against DPP homolog 1; SMAD, mothers against DPP homolog 1; MAD, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1; transforming growth factor-beta signaling protein 1; transforming growth factor-beta-signaling protein 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | JV4-1; Mad-related protein 1; SMAD family member 1; SMAD 1; Smad1; hSMAD1; Transforming growth factor-beta-signaling protein 1; BSP-1 |
| Protein Family: | Mothers against decapentaplegic |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SMAD1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SMAD1_HUMAN |