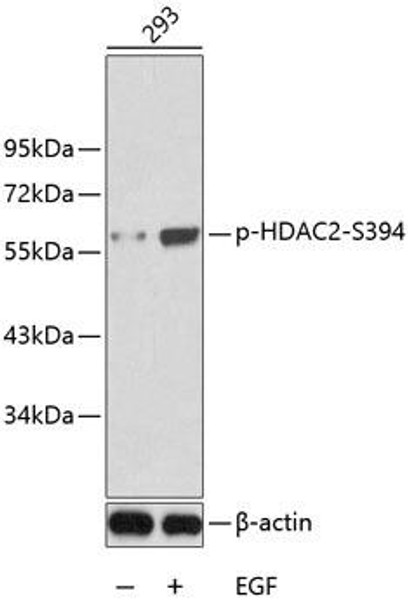
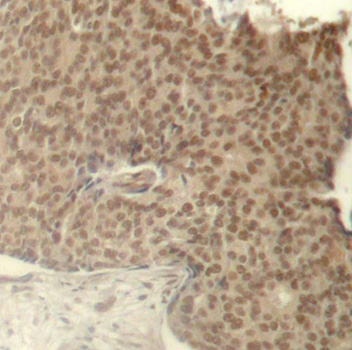
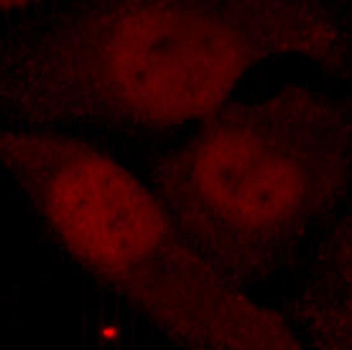
Anti-Phospho-HDAC2-S394 Antibody (CABP0201)
- SKU:
- CABP0201
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Application:
- WB
- Application:
- IHC
- Application:
- IF
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-Phospho-HDAC2-S394 Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CABP0201 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 100 uL |
| 申し込み: | WB IHC IF |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S394 of human HDAC2 |
| 申し込み: | WB IHC IF |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:100 IF 1:100 - 1:200 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| ポジティブサンプル: | 293 |
| 免疫原: | A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S394 of human HDAC2 |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | Email for sequence |
| 遺伝子ID: | 3066 |
| Uniprot: | Q92769 |
| セルラーロケーション: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| 計算された分子量: | 51kDa/55kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 60kDa |
| 同義語: | HD2, RPD3, YAF1, HDAC2 |
| バックグラウンド: | This gene product belongs to the histone deacetylase family. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes, and are responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues at the N-terminal regions of core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). This protein forms transcriptional repressor complexes by associating with many different proteins, including YY1, a mammalian zinc-finger transcription factor. Thus, it plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HDAC2: a transcriptional regulator of the histone deacetylase family, subfamily 1. Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation plays a role in epigenetic repression and transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 3.5.1.98; Transcription, coactivator/corepressor; Deacetylase; Nuclear receptor co-regulator Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 6q21 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; heterochromatin; transcription factor complex; protein complex; Sin3 complex; ESC/E(Z) complex; cytoplasm; nuclear chromatin; replication fork; NuRD complex; nucleus Molecular Function:deacetylase activity; nucleosomal DNA binding; protein deacetylase activity; transcription factor binding; NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity (H3-K9 specific); protein binding; enzyme binding; NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity (H3-K14 specific); sequence-specific DNA binding; heat shock protein binding; chromatin binding; NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity (H4-K16 specific); histone deacetylase activity; transcription factor activity Biological Process: establishment and/or maintenance of chromatin architecture; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of proteolysis; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; regulation of gene expression, epigenetic; negative regulation of cell cycle; cardiac muscle cell development; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation; negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic; positive regulation of cell proliferation; dendrite development; circadian regulation of gene expression; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation; response to drug; transcription, DNA-dependent; negative regulation of transcription factor activity; hippocampus development; histone deacetylation; regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; response to cocaine; odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth; chromatin remodeling; maintenance of chromatin silencing; negative regulation of MHC class II biosynthetic process; ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling; epidermal cell differentiation; positive regulation of transcription factor activity; gene expression; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; embryonic digit morphogenesis; blood coagulation; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; negative regulation of apoptosis |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene product belongs to the histone deacetylase family. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes, and are responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues at the N-terminal regions of core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). This protein forms transcriptional repressor complexes by associating with many different proteins, including YY1, a mammalian zinc-finger transcription factor. Thus, it plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010] |
| UniProt Code: | Q92769 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 68068066 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3066 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q92769.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q92769,Q5SRI8, Q5SZ86, Q8NEH4, B3KRS5, B4DL58, E1P561 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q92769 |
| Molecular Weight: | 488 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Histone deacetylase 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | histone deacetylase 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HDAC2 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HD2; RPD3; YAF1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | histone deacetylase 2; YY1-associated factor 1; transcriptional regulator homolog RPD3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Histone deacetylase 2 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HDAC2 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | HDAC2_HUMAN |