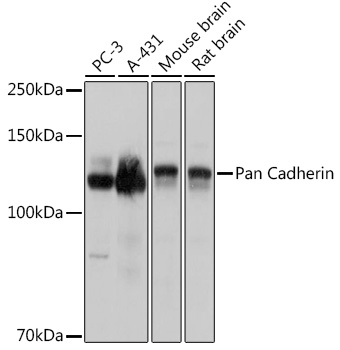
| バックグラウンド: | Cadherin is one of a class of integral-membrane glycoproteins that are involved in cell to cell attachment for preserving the integrity of all solid tissues. Cadherins have three major regions: the Ca2+ -dependent extracellular region that mediates adhesion (cadherin to cadherin) for cell to cell binding; the transmembrane region; and the cytoplasmic region that extends into the cell and interacts with catenins, which in turn are linked to the actin of the cytoskeleton. Cadherins are differentially expressed during development and in adult organs. Since many cell types express multiple cadherin subclasses simultaneously (the combination differs with cell type), it can be inferred that the adhesion properities of individual cells are thus governed by varying the combinations of cadherins. Altered expression of cadherins are involved in invasion and metastasis of tumour cells. The classical cadherins (e.g. E-, N-, and P-cadherins) are the most common family members. E-cadherin (also known as uvomorulin) is concentrated in the belt desmosome in epithelial cells; N-cadherin is found in nerve, muscle, and lens cells and helps maintain the integrity of neuronal aggregates; P-cadherin is expressed in placental and epidermal cells. |