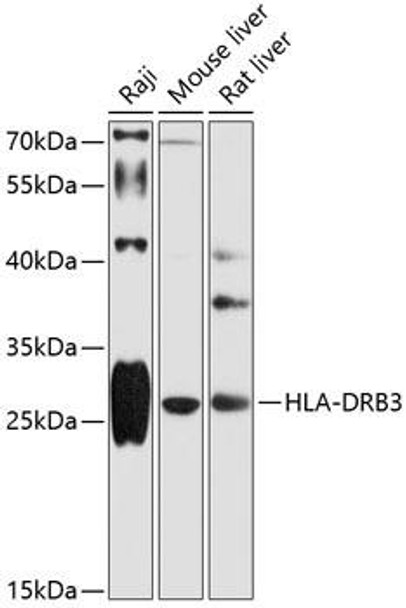
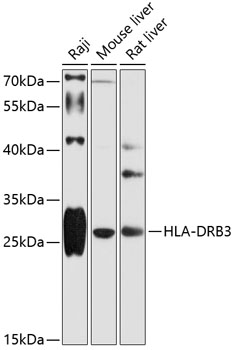
Anti-HLA-DRB3 Antibody (CAB12444)
- SKU:
- CAB12444
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Research Area:
- Immunology
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-HLA-DRB3 Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CAB12444 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 30-227 of human HLA-DRB3 (NP_072049.2). |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| ポジティブサンプル: | Raji, Mouse liver, Rat liver |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 30-227 of human HLA-DRB3 (NP_072049.2). |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | GDTR PRFL ELRK SECH FFNG TERV RYLD RYFH NQEE FLRF DSDV GEYR AVTE LGRP VAES WNSQ KDLL EQKR GRVD NYCR HNYG VGES FTVQ RRVH PQVT VYPA KTQP LQHH NLLV CSVS GFYP GSIE VRWF RNGQ EEKA GVVS TGLI QNGD WTFQ TLVM LETV PRSG EVYT CQVE HPSV TSAL TVEW RARS ESAQ SK |
| 遺伝子ID: | 3125 |
| Uniprot: | P79483 |
| セルラーロケーション: | Cell membrane, Endoplasmic reticulum membrane, Endosome membrane, Golgi apparatus, Late endosome membrane, Lysosome membrane, Single-pass type I membrane protein, trans-Golgi network membrane |
| 計算された分子量: | 29kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 30kDa |
| 同義語: | HLA-DRB3, HLA-DR1B, HLA-DR3B, major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 3 |
| バックグラウンド: | HLA-DRB3 belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DRA) and a beta (DRB) chain, both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa and its gene contains 6 exons. Exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and exon 5 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. Within the DR molecule the beta chain contains all the polymorphisms specifying the peptide binding specificities. Typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow and kidney transplantation. DRB1 is expressed at a level five times higher than its paralogues DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. The presence of DRB3 is linked with allelic variants of DRB1, otherwise it is omitted. There are 4 related pseudogenes: DRB2, DRB6, DRB7, DRB8 and DRB9. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HLA-DRB3: Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accommodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route, where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules, and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments, exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides, autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs, other cells of the gastrointestinal tract, such as epithelial cells, express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs, which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen, three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form a heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs, CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases, including CTSS and CTSL, leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B-cells, the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal miroenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules, increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading. Belongs to the MHC class II family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 6p21.3 Cellular Component: Golgi membrane; membrane; late endosome membrane; lysosomal membrane; integral to plasma membrane; plasma membrane; trans-Golgi network membrane; external side of plasma membrane; MHC class II protein complex Molecular Function:MHC class II receptor activity; protein binding; peptide antigen binding Biological Process: humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin; T-helper 1 type immune response; inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus; negative regulation of T cell proliferation; detection of bacterium; regulation of interleukin-4 production; negative regulation of interferon-gamma production; cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; T cell costimulation; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II; immune response; immunoglobulin production during immune response; signal transduction; T cell receptor signaling pathway; protein tetramerization |
| NCBI Summary: | HLA-DRB3 belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DRA) and a beta (DRB) chain, both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa and its gene contains 6 exons. Exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and exon 5 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. Within the DR molecule the beta chain contains all the polymorphisms specifying the peptide binding specificities. Typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow and kidney transplantation. DRB1 is expressed at a level five times higher than its paralogues DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. The presence of DRB3 is linked with allelic variants of DRB1, otherwise it is omitted. There are 4 related pseudogenes: DRB2, DRB6, DRB7, DRB8 and DRB9. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P79483 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 34395491 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3125 |
| NCBI Accession: | P79483.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P13761,P79483 |
| Molecular Weight: | 29kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR beta 3 chain |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HLA-DRB3 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DRB3; HLA-DPB1; HLA-DR1B; HLA-DR3B |
| NCBI Protein Information: | major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR beta 3 chain |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | MHC class II antigen DRB3 |
| Protein Family: | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HLA-DRB3 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DRB3_HUMAN |