Anti-GGCX Antibody (CAB1806)
- SKU:
- CAB1806
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Frequently bought together:
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-GGCX Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CAB1806 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 479-758 of human GGCX (NP_000812.2). |
| 申し込み: | WB |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse |
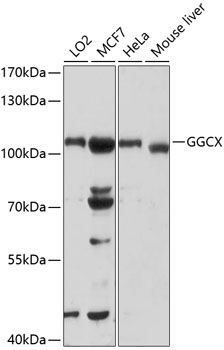
| ポジティブサンプル: | LO2, MCF7, HeLa, Mouse liver |
| 免疫原: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 479-758 of human GGCX (NP_000812.2). |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | QRIF DPRV DIVQ AAWS PFQR TSWV QPLL MDLS PWRA KLQE IKSS LDNH TEVV FIAD FPGL HLEN FVSE DLGN TSIQ LLQG EVTV ELVA EQKN QTLR EGEK MQLP AGEY HKVY TTSP SPSC YMYV YVNT TELA LEQD LAYL QELK EKVE NGSE TGPL PPEL QPLL EGEV KGGP EPTP LVQT FLRR QQRL QEIE RRRN TPFH ERFF RFLL RKLY VFRR SFLM TCIS LRNL ILGR PSLE QLAQ EVTY ANLR PFEA VGEL NPSN TDSS HSNP PESN PDPV HSEF |
| 遺伝子ID: | 2677 |
| Uniprot: | P38435 |
| セルラーロケーション: | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane, Multi-pass membrane protein |
| 計算された分子量: | 80kDa/87kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 110kDa |
| 同義語: | GGCX, VKCFD1 |
| バックグラウンド: | This gene encodes an integral membrane protein of the rough endoplasmic reticulum that carboxylates glutamate residues of vitamin K-dependent proteins to gamma carboxyl glutamate, a modification that is required for their activity. The vitamin K-dependent protein substrates have a propeptide that binds the enzyme, with carbon dioxide, dioxide, and reduced vitamin K acting as co-substrates. Vitamin K-dependent proteins affect a number of physiologic processes including blood coagulation, prevention of vascular calcification, and inflammation. Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like disorder with associated multiple coagulation factor deficiency. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | GGCX: Mediates the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of glutamate residues to calcium-binding gamma-carboxyglutamate (Gla) residues with the concomitant conversion of the reduced hydroquinone form of vitamin K to vitamin K epoxide. Defects in GGCX are a cause of combined deficiency of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors type 1 (VKCFD1); also known as multiple coagulation factor deficiency III (MCFD3). VKCFD leads to a bleeding tendency that is usually reversed by oral administration of vitamin K. Defects in GGCX are the cause of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like disorder with multiple coagulation factor deficiency (PXEL-MCFD). This syndrome is characterized by hyperlaxity of the skin involving the entire body. Important phenotypic differences with classical PXE include much more severe skin laxity with spreading toward the trunk and limbs with thick, leathery skin folds rather than confinement to flexural areas, and no decrease in visual acuity. Moreover, detailed electron microscopic analyzes revealed that alterations of elastic fibers as well as their mineralization are slightly different from those in classic PXE. Belongs to the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 4.1.1.90; Lyase; Membrane protein, integral; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Ligase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2p12 Cellular Component: endoplasmic reticulum membrane; membrane Molecular Function:gamma-glutamyl carboxylase activity Biological Process: blood coagulation; peptidyl-glutamic acid carboxylation; protein modification process Disease: Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum-like Disorder With Multiple Coagulation Factor Deficiency; Vitamin K-dependent Clotting Factors, Combined Deficiency Of, 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes an integral membrane protein of the rough endoplasmic reticulum that carboxylates glutamate residues of vitamin K-dependent proteins to gamma carboxyl glutamate, a modification that is required for their activity. The vitamin K-dependent protein substrates have a propeptide that binds the enzyme, with carbon dioxide, dioxide, and reduced vitamin K acting as co-substrates. Vitamin K-dependent proteins affect a number of physiologic processes including blood coagulation, prevention of vascular calcification, and inflammation. Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like disorder with associated multiple coagulation factor deficiency. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P38435 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 84028279 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2677 |
| NCBI Accession: | P38435.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P38435,Q14415, Q6GU45, B4DMC5, E9PEE1, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P38435 |
| Molecular Weight: | 80,989 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | gamma-glutamyl carboxylase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GGCX |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | VKCFD1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase; Peptidyl-glutamate 4-carboxylase; Vitamin K gamma glutamyl carboxylase |
| Protein Family: | Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GGCX |
| UniProt Entry Name: | VKGC_HUMAN |