Anti-CNTN1 Antibody (CAB17459)
- SKU:
- CAB17459
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Reactivity:
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
Frequently bought together:
Description
| 抗体名: | Anti-CNTN1 Antibody |
| 抗体コード: | CAB17459 |
| 抗体サイズ: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| 申し込み: | WB IHC |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 宿主種: | Rabbit |
| 免疫原: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 250-350 of human CNTN1 (NP_778203.1). |
| 申し込み: | WB IHC |
| 推奨希釈: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| 反応性: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
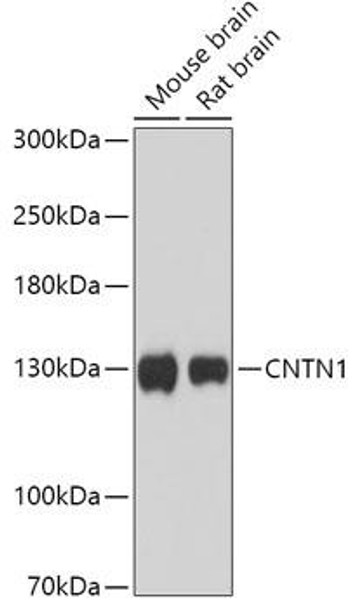
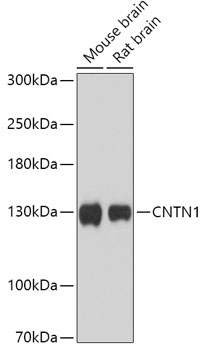
| ポジティブサンプル: | Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| 免疫原: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 250-350 of human CNTN1 (NP_778203.1). |
| 精製方法: | Affinity purification |
| ストレージバッファ: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| アイソタイプ: | IgG |
| 順序: | LECF ALGN PVPD IRWR KVLE PMPS TAEI STSG AVLK IFNI QLED EGIY ECEA ENIR GKDK HQAR IYVQ AFPE WVEH INDT EVDI GSDL YWPC VATG KPIP T |
| 遺伝子ID: | 1272 |
| Uniprot: | Q12860 |
| セルラーロケーション: | |
| 計算された分子量: | 70kDa/111kDa/113kDa |
| 観察された分子量: | 130kDa |
| 同義語: | CNTN1, F3, GP135, MYPCN |
| バックグラウンド: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored neuronal membrane protein that functions as a cell adhesion molecule. It may play a role in the formation of axon connections in the developing nervous system. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011] |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CNTN1: Contactins mediate cell surface interactions during nervous system development. Involved in the formation of paranodal axo-glial junctions in myelinated peripheral nerves and in the signaling between axons and myelinating glial cells via its association with CNTNAP1. Participates in oligodendrocytes generation by acting as a ligand of NOTCH1. Its association with NOTCH1 promotes NOTCH1 activation through the released notch intracellular domain (NICD) and subsequent translocation to the nucleus. Interaction with TNR induces a repulsion of neurons and an inhibition of neurite outgrowth. Defects in CNTN1 are the cause of Compton-North congenital myopathy (CNCM). CNCM is a familial lethal form of congenital onset muscle weakness, inherited in an autosomal-recessive fashion and characterized by a secondary loss of beta2-syntrophin and alpha-dystrobrevin from the muscle sarcolemma, central nervous system involvement, and fetal akinesia. Belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Contactin family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell adhesion; Membrane protein, GPI anchor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12q11-q12 Cellular Component: membrane Disease: Myopathy, Congenital, Compton-north |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored neuronal membrane protein that functions as a cell adhesion molecule. It may play a role in the formation of axon connections in the developing nervous system. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | Q12860 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 2497301 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1272 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q12860.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q12860,Q12861, Q14030, Q7M4P0, Q8N466, A8K0H9, A8K0Y3 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q12860 |
| Molecular Weight: | 70,604 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Contactin-1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | contactin 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CNTN1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | F3; GP135; MYPCN |
| NCBI Protein Information: | contactin-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Contactin-1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Glycoprotein gp135; Neural cell surface protein F3 |
| Protein Family: | Contactin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CNTN1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CNTN1_HUMAN |