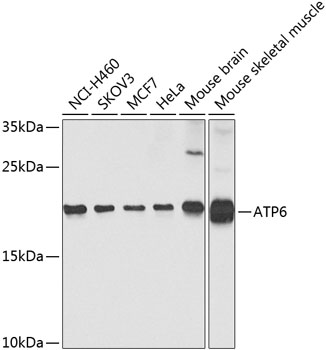
| UniProt Protein Function: | ATP6: Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Key component of the proton channel; it may play a direct role in the translocation of protons across the membrane. Defects in MT-ATP6 are the cause of neurogenic muscle weakness, ataxia, and retinitis pigmentosa (NARP). Defects in MT-ATP6 are a cause of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON). LHON is a maternally inherited disease resulting in acute or subacute loss of central vision, due to optic nerve dysfunction. Cardiac conduction defects and neurological defects have also been described in some patients. LHON results from primary mitochondrial DNA mutations affecting the respiratory chain complexes. Defects in MT-ATP6 are a cause of Leigh syndrome (LS). LS is a severe neurological disorder characterized by bilaterally symmetrical necrotic lesions in subcortical brain regions. Defects in MT-ATP6 are a cause of mitochondrial infantile bilateral striatal necrosis (MIBSN). Bilateral striatal necrosis is a neurological disorder resembling Leigh syndrome. Belongs to the ATPase A chain family.Protein type: Transporter, ion channel; Membrane protein, multi-pass; Transporter; Membrane protein, integral; MitochondrialCellular Component: mitochondrion; membrane; proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, coupling factor F(o); mitochondrial inner membrane; integral to membraneMolecular Function: hydrogen ion transmembrane transporter activityBiological Process: ATP synthesis coupled proton transport; proton transport; transport; ATP biosynthetic process; ion transport |